Salivary gland tumors are growths of abnormal cells (tumors) that begin in the salivary glands. Salivary gland tumors are rare.
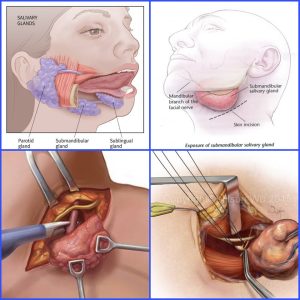
Salivary glands make saliva, which aids in digestion, keeps your mouth moist and supports healthy teeth. You have three pairs of major salivary glands under and behind your jaw — parotid, sublingual and submandibular. Many other tiny salivary glands are in your lips, inside your cheeks, and throughout your mouth and throat.
Salivary gland tumors can begin in any of your salivary glands. Most are noncancerous (benign), but sometimes they can be cancerous. Most salivary gland tumors occur in the parotid glands.
Treatment for salivary gland tumors is usually with surgery to remove the tumor. People with salivary gland cancers may need additional treatments.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a salivary gland tumor may include:
- A lump or swelling on or near your jaw or in your neck or mouth
- Numbness in part of your face
- Muscle weakness on one side of your face
- Persistent pain in the area of a salivary gland
- Difficulty swallowing
- Trouble opening your mouth widely
Case review of the day:
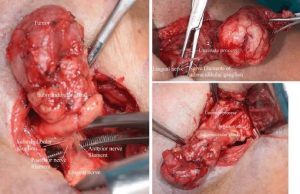
41 year old male
Submandibular mass right for 3 years
Movable, non tender, 6 cms in widest diameter, no palpable cervical lymph nodes
Ct scan of the neck revealed:
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any persistent signs or symptoms that worry you.




