A total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (TAHBSO) is a surgical procedure that combines several components:
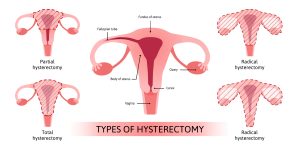
- Hysterectomy:
- A hysterectomy involves the removal of the uterus and cervix.
- The term “abdominal” refers to the surgical technique used, which means the surgery is performed through an incision in your abdomen.
- After a hysterectomy, you will no longer have periods or be able to become pregnant.
- Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy:
- This part of the procedure involves removing both of your ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- The surgeon will perform the hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy during the same operation.
- Reasons for this surgery may include heavy periods, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, cancer, or if you are at high risk for ovarian cancer.
- Procedure Details:
- Before the surgery, you will receive general anesthesia to sleep.
- The incision may be made either vertically or horizontally in your lower abdomen.
- The surgeon will remove your uterus, cervix, ovaries, and/or fallopian tubes through this incision.
- Risks include bleeding during surgery, infection, damage to surrounding organs, and the possibility of needing further surgery.
- Recovery:
- After surgery, you’ll typically stay in the hospital for about 2 nights.
- Expect a full recovery to take approximately 6 weeks.
- Vaginal bleeding and discharge are normal for 1 to 2 weeks after surgery.
- Avoid strenuous exercise, heavy lifting, and sexual activity for 6 weeks post-surgery.
- Contact your provider if you experience fever, severe nausea, heavy bleeding, or other concerning symptoms.
Remember to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and attend pre- and post-op appointments. If you have any further questions, feel free to ask!