Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that affects the lungs, pancreas, liver, intestines, sinuses, and sex organs. It’s caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, which leads to the production of thick, sticky mucus in the body. This mucus can clog the airways and ducts in various organs, leading to serious respiratory and digestive problems.
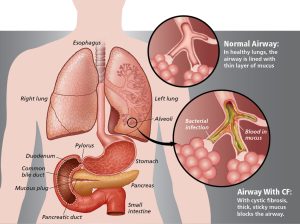
Symptoms:
- Persistent cough with thick mucus
- Frequent lung infections, such as pneumonia or bronchitis
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
- Poor growth and weight gain despite a good appetite
- Frequent sinus infections
- Greasy or bulky stools
- Difficulty breathing
- Chronic fatigue
Cause: Cystic fibrosis is caused by inheriting two faulty copies of the CFTR gene, one from each parent. These mutations disrupt the function of the CFTR protein, which regulates the flow of salt and fluids in and out of cells. As a result, thick, sticky mucus builds up in various organs, leading to the symptoms associated with CF.
Prevention: Since cystic fibrosis is a genetic condition, it cannot be prevented. However, genetic testing and counseling can help individuals understand their risk of passing the CF gene to their children. Prenatal testing is also available for couples who have a family history of CF or are carriers of the CF gene.
Treatment: While there is no cure for cystic fibrosis, treatment aims to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Bronchodilators, antibiotics, mucolytics, and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to help manage respiratory symptoms and prevent lung infections.
- Airway clearance techniques: These techniques, such as chest physiotherapy and using devices like a vibrating vest or a handheld device called a positive expiratory pressure (PEP) mask, help loosen and clear mucus from the airways.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve lung function and overall health in individuals with CF.
- Nutritional therapy: A high-calorie, high-fat diet and pancreatic enzyme supplements may be recommended to help individuals with CF maintain a healthy weight and absorb essential nutrients.
- Lung transplant: In severe cases of lung disease, lung transplantation may be considered as a treatment option.
Research into new treatments and therapies for cystic fibrosis, including gene therapy and drugs that target the underlying cause of the disease, is ongoing, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with CF.



