Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils, which are two small glands located in the back of the throat. Here’s an overview of tonsillectomy, including symptoms, causes, treatments, and prevention:
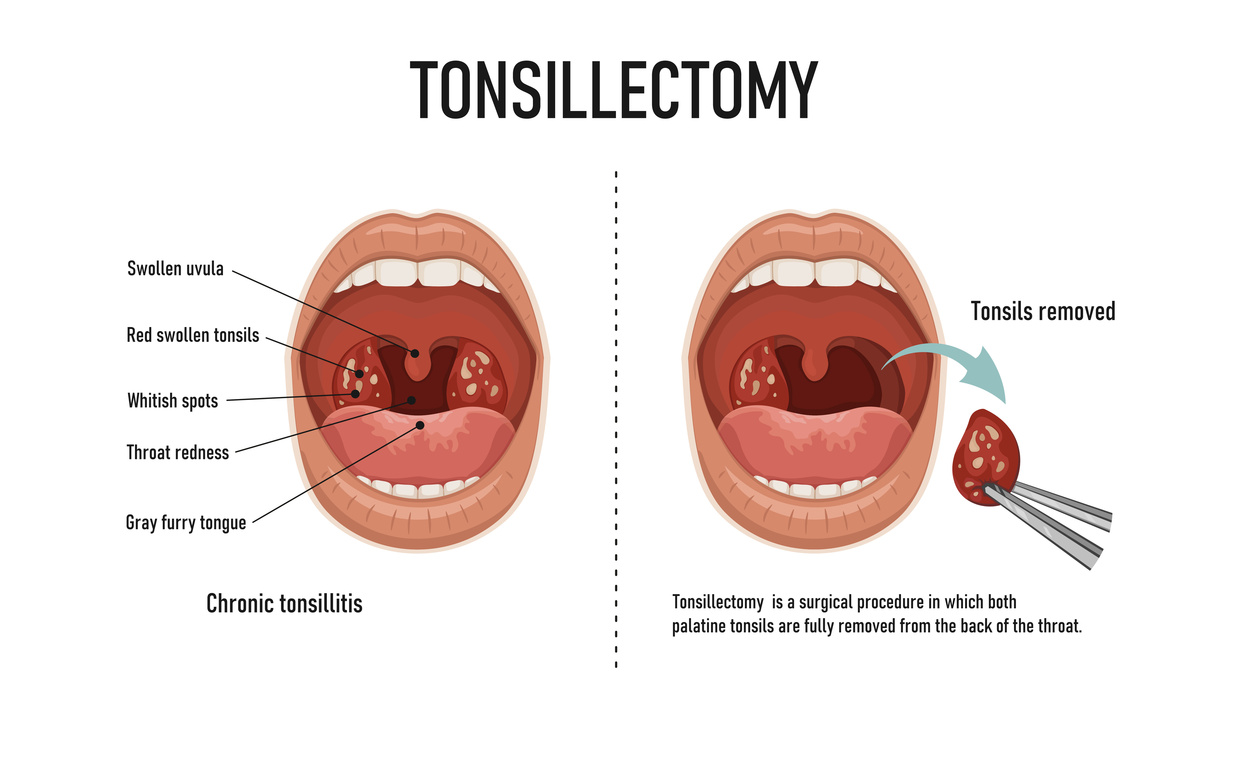
Symptoms:
- Recurrent or chronic throat infections (tonsillitis), characterized by sore throat, fever, swollen glands, and difficulty swallowing.
- Enlarged tonsils that obstruct breathing or cause sleep disturbances, such as snoring or sleep apnea.
- Persistent or recurrent bacterial infections, such as streptococcal infections, despite antibiotic treatment.
Causes:
- Bacterial or viral infections: Tonsillitis is often caused by bacteria, such as Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococcus), or viruses like adenovirus or Epstein-Barr virus.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can lead to inflammation of the tonsils.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to irritants or pollutants in the air may contribute to tonsil inflammation.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to recurrent tonsillitis or enlarged tonsils.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics: In cases of bacterial tonsillitis, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear the infection.
- Tonsillectomy: Surgical removal of the tonsils is recommended for recurrent or severe cases of tonsillitis, persistent throat infections, or obstructive sleep apnea.
Prevention:
- Good hygiene practices: Regular handwashing can help prevent the spread of infections that can lead to tonsillitis.
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections, especially if they are coughing or sneezing.
- Strengthening the immune system through a healthy diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management.
- Managing allergies: Identifying and avoiding allergens can reduce the risk of allergic reactions that contribute to tonsil inflammation.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment recommendations based on individual circumstances. Tonsillectomy is typically considered after other treatment options have been exhausted or if there are specific indications for surgical intervention.