A CT-guided lung biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure used to obtain small tissue samples from the lung for diagnostic purposes.
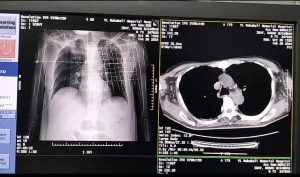
1. Preparation:
- Before the procedure, the patient may need to undergo certain tests such as blood tests or imaging scans to assess their overall health and the location of the abnormality in the lung.
- The patient will be asked to refrain from eating or drinking for a certain period of time before the procedure.
2. Patient Positioning:
- The patient will be positioned on an examination table, depending on the location of the abnormality in the lung.
3. CT Scan:
- A CT scanner will be used to create detailed images of the lung and guide the biopsy needle to the precise location of the abnormal tissue.
- The patient may need to hold their breath briefly during the CT scan to minimize motion and ensure accurate imaging.
4. Local Anesthesia:
- The skin overlying the biopsy site will be cleaned and numbed with a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
5. Biopsy Needle Insertion:
- Once the area is numb, the interventional radiologist or pulmonologist will insert a thin needle through the skin and into the lung tissue under CT guidance.
- The CT images help the doctor guide the needle to the exact location of the abnormal tissue while avoiding nearby structures such as blood vessels.
6. Tissue Sample Collection:
- Once the needle is in position, small tissue samples (biopsies) will be collected using a biopsy needle.
- Multiple samples may be taken to increase the chances of obtaining enough tissue for an accurate diagnosis.
7. Post-Procedure Care:
- After the biopsy, pressure may be applied to the biopsy site to minimize bleeding.
- The patient will be monitored for a brief period following the procedure to ensure there are no immediate complications.
8. Recovery:
- Most patients can resume normal activities shortly after the procedure, although some may experience mild discomfort or soreness at the biopsy site.
- Results from the biopsy are typically available within a few days to a week, depending on the specific laboratory procedures.
CT-guided lung biopsy is generally considered safe and effective for obtaining tissue samples from the lung with minimal risk to the patient. However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications, such as bleeding, infection, or pneumothorax, which should be discussed with the patient prior to the procedure.



