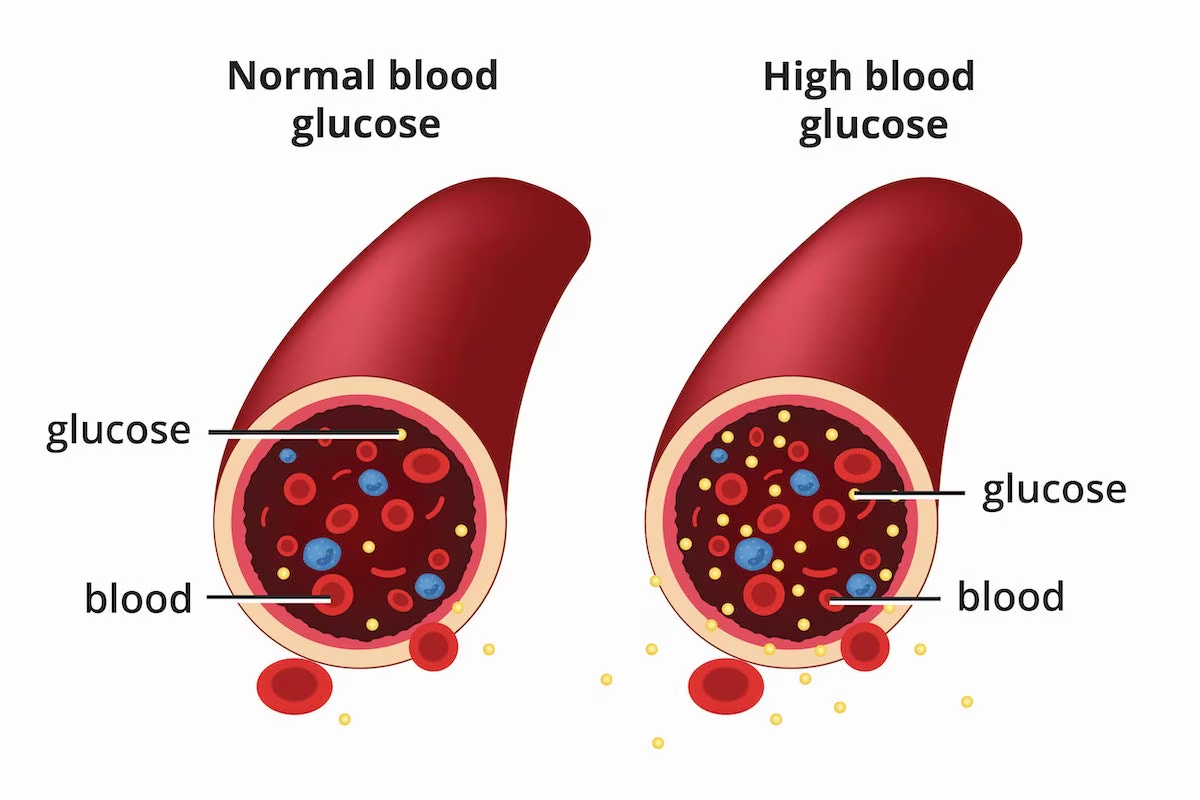
Managing and preventing diabetes involves a combination of healthy lifestyle choices, regular monitoring, and sometimes medication, depending on the type of diabetes. There are two main types: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, with Type 2 being more preventable and manageable through lifestyle changes. Here’s a breakdown of key strategies for both prevention and management:
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
- Healthy Diet:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Limit refined sugars and processed foods: Avoid sugary snacks, sodas, and fast food to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Portion control: Eating in moderation helps prevent overeating and excess sugar intake.
- Fiber-rich foods: Include foods high in fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grains) to help control blood sugar levels.
- Avoid excessive alcohol: Alcohol can raise blood sugar and should be consumed in moderation.
- Physical Activity:
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise (e.g., brisk walking) per week, along with strength training twice a week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Losing even a small percentage of body weight (5-10%) can significantly reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:
- Regularly check blood sugar levels if you’re at high risk (e.g., overweight, family history, or have prediabetes) to catch any early signs of diabetes.
- Manage Stress:
- High stress can contribute to unhealthy behaviors (like overeating) and negatively affect blood sugar levels. Practice stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Quit Smoking:
- Smoking increases the risk of diabetes and can also exacerbate complications for people already diagnosed with the condition.
- Get Enough Sleep:
- Poor sleep or inadequate sleep increases the risk of developing diabetes. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Managing Diabetes
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:
- Regular monitoring is crucial to keep blood sugar levels within the target range. This may involve using a glucometer or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM).
- Medication:
- For people with Type 2 diabetes, medications (e.g., metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin) may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin therapy as the body cannot produce insulin.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding medication and insulin.
- Dietary Modifications:
- Carb counting: Learn to manage your carbohydrate intake, as carbs directly impact blood sugar levels.
- Low glycemic index foods: Choose foods that have a lower glycemic index (e.g., whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables) to avoid rapid blood sugar spikes.
- Small, frequent meals: This can help keep blood sugar levels stable throughout the day.
- Exercise:
- Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar. It can be particularly helpful in managing Type 2 diabetes.
- Stay active: Aim for activities that you enjoy and can do consistently, such as walking, swimming, or biking.
- Regular Checkups and Monitoring:
- Regular medical checkups are essential for managing diabetes and checking for any complications (e.g., eye problems, kidney issues, or nerve damage).
- Keep track of HbA1c (average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months) to monitor long-term blood sugar control.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drinking plenty of water helps with blood sugar regulation and prevents dehydration, which can be a concern with diabetes.
- Manage Associated Health Conditions:
- Keep high blood pressure and cholesterol levels under control, as these are often linked to diabetes and can increase the risk of complications.
- Support and Education:
- Joining a diabetes support group or working with a diabetes educator can help you stay on track with your management plan and provide emotional support.
Conclusion
Managing and preventing diabetes requires a holistic approach involving lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and, in some cases, medications. If you’re at risk for Type 2 diabetes, adopting healthy habits early on can help prevent the onset of the disease. For those with diabetes, maintaining a consistent routine of healthy eating, exercise, and monitoring is crucial for long-term health and well-being. Always consult with healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan.