Photorefractive Keratectomy (PRK) is a type of refractive surgery that uses a laser to treat vision problems caused by refractive errors. Here are the key details about PRK:
- Purpose and Procedure:
- PRK aims to correct refractive errors by changing the shape of the cornea using a laser.
- Unlike LASIK, PRK does not involve creating a flap in the cornea.
- The procedure precisely removes and sculpts corneal tissue at the microscopic level using a computer-generated, cold laser beam.
- Indications:
- PRK is used to treat:
- Myopia (nearsightedness)
- Hyperopia (farsightedness)
- Astigmatism
- PRK is used to treat:
- Candidate Requirements:
- You should be 18 years or older (ideally over 21 when vision stabilizes).
- Your eye prescription should not have changed in the last year.
- Healthy corneas and overall good eye health are necessary.
- Realistic expectations about PRK outcomes are essential.
- Advantages:
- PRK is suitable for people with dry eyes or thin corneas.
- It’s a better option for those with an active lifestyle or specific job requirements.
- No corneal flap is created, reducing the risk of accidental flap dislodgement.
- Examination Process:
- Your ophthalmologist will:
- Check overall eye health.
- Measure corneal thickness.
- Assess pupil size.
- Measure refractive error.
- Your ophthalmologist will:
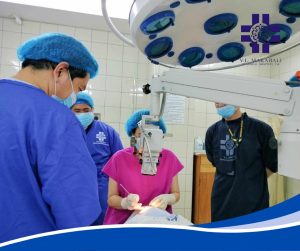
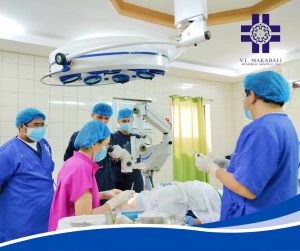

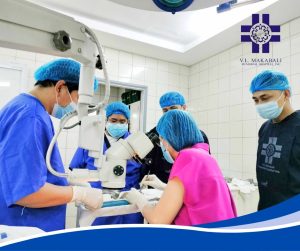
Salute indeed to Dr. Mah-Sadorra and the entire Operating Room (OR) staff for their skill, dedication, and teamwork in carrying out a successful procedure. Wishing the patient a smooth recovery and continued good health.



